CONDYLAR RESORPTION
Bone loss at the mandibular condyle has been described as a result of orthognathic surgery, systemic and local arthritides, post-traumatic remodeling, and/or hormonal imbalance.
Osseous condylar resorption that occurs without an obvious cause is termed idiopathic condylar resorption (ICR). Condylar resorption can be aggressive (months) or slow (years).
The signs of condylar resorption are:
Facial imbalance (receding chin),
Smaller airway (snoring, apnea) and
Bite disturbances (anterior open bite, posterior tooth wear and muscle pain).
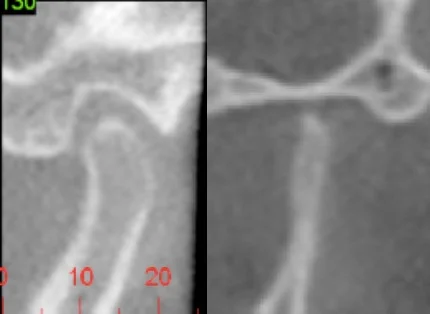
In the CBCT patient here you can see a normal mandibular condyle on the bottom and one with condylar resorption (from rheumatoid arthritis) on top. Notice not just the changes to the condyle itself but the fossa has been flattened and thinned.
Modern treatments for condylar resorption almost exclusively focus on the surgical resection of the diseased joint and replacing it with an artificial joint prosthesis. Our approach however follows the successful medical protocols seen in the fields of rheumatology and orthopedics. We take the time to identify the true contributors to the patient condylar resorption and treat those.

—Dr. Michael Gunson
Causes of condylar resorption
Systemic factors and compressive factors.
Anything that compresses the TMJ (bad bite, bad dentistry, bad orthognathic surgery, bruxism, repetitive oral habits, etc.) will cause bone changes through inflammation.
Any systemic condition that raises inflammation in the body (arthritis, low estrogen, anorexia, infections, etc) will exacerbate the resorption caused by compression. Both sides of the equation require treatment.
To learn more about Cause of Condylar Resorption, you can read our publication "Risk Factors in the Initiation of Condylar Resorption" by G. William Arnett, DDS, FACD,* and Michael J. Gunson, DDS, MD © 2013 Published by Elsevier Inc.
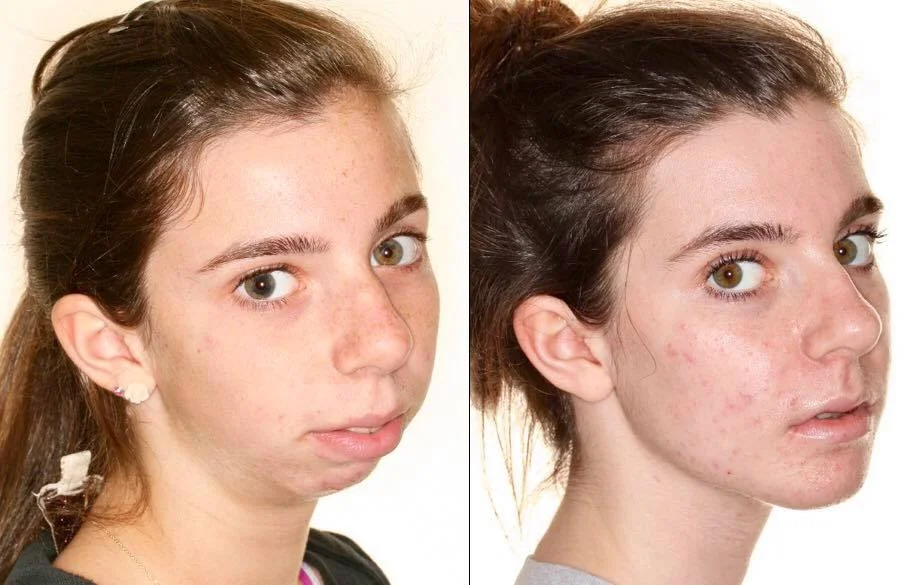
Treatment Case Study
Treatment requires removing compression by fixing the bite and reducing the influence of whole body inflammation on the TMJ.
This patient has rheumatoid arthritis with condylar resorption.
Her pre surgical and post surgical medical regimen consisted of Vitamin D and calcium for bone health, doxycycline to protect the bone and cartilage, fish oil as an anti-inflammatory, Celebrex as an anti-inflammatory and Enbrel as an antirheumatologic agent.
She is 2 years post surgery in the photo and presently only takes the over the counter supplements as the compression has been treated and her systemic inflammation is quiescent.